Oil-Immersed vs Dry-Type Transformers: Why Power Systems Prefer Oil-Cooled Solutions
Time:2025-05-21 Auther:ZTelec-www.ztelectransformer.com
Transformers are essential in modern power transmission and distribution, directly impacting the stability of the power grid. Oil-immersed transformers have long been the dominant choice—from urban power supply to ultra-high voltage transmission projects. Although dry-type transformers are used in some specific environments due to their environmental and fire safety benefits, oil-immersed transformers stand out in performance, cost, and application scope. This article analyzes why power systems prefer oil-immersed transformers based on technical features, cost efficiency, application scenarios, and system adaptability.
Heat Dissipation and Overload Performance
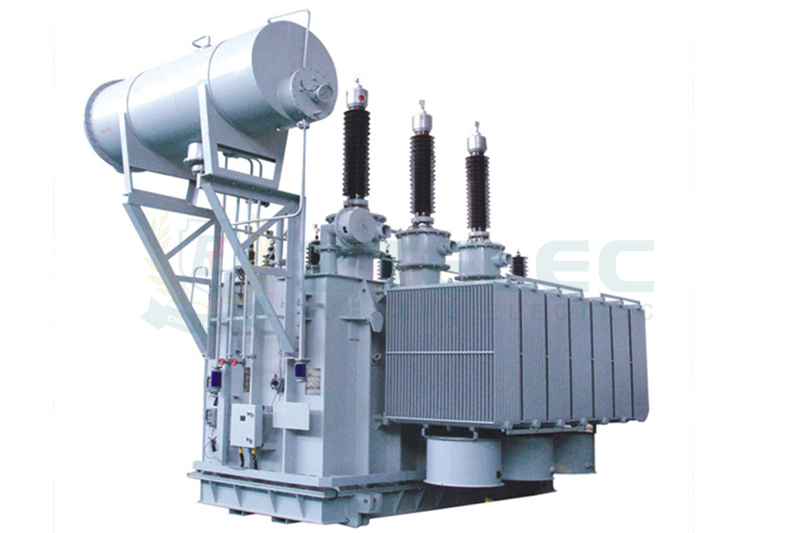
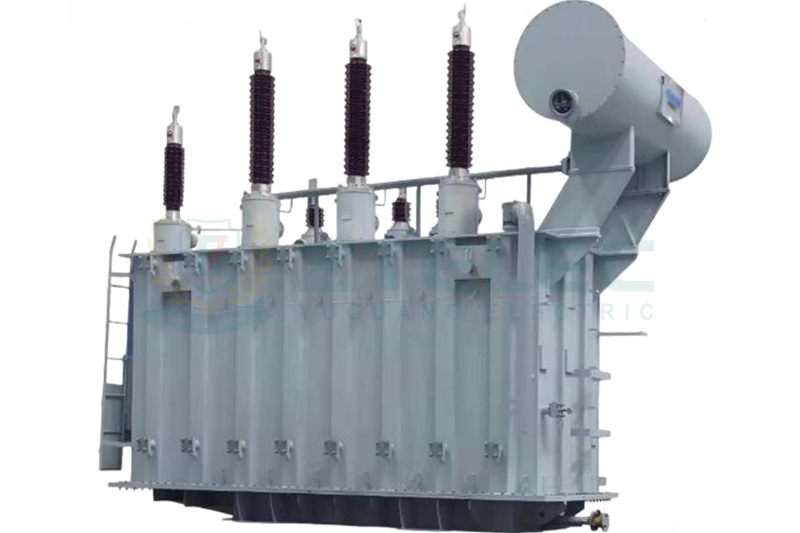
During operation, transformers generate significant heat. use insulating oil with superior heat transfer and storage capabilities, allowing them to operate efficiently under high loads for extended periods. This makes them ideal for large-capacity, high-voltage environments such as ultra-high voltage transmission lines and large power plants.
In high-temperature conditions, oil-immersed transformers maintain stability without requiring extra cooling equipment, unlike dry-type transformers that need fans or additional devices. They also have stronger overload tolerance, ensuring continuous power during peak demand or sudden surges, reducing failure and outage risks.
Life Cycle Cost Comparison
Dry-type transformers typically have 30%-50% higher initial purchase costs compared to oil-immersed transformers. While dry types require less daily maintenance, oil-immersed transformers, with proper oil replacement and filtration, can last 20-40 years, surpassing dry transformers in longevity.
For example, in a large industrial park, although dry-type transformers increase upfront costs, oil-immersed transformers reduce long-term expenses due to fewer replacements and better reliability, proving more economical over the entire life cycle.

Application Scenarios and Cost Performance
Oil-immersed transformers excel in outdoor, large-capacity, and high-load environments. They are commonly used in power projects above 110kV and capacities over 10MVA, including substations and industrial parks, where performance and reliability are critical.
Their design facilitates easier inspection and maintenance, and their reasonable price makes them suitable for power infrastructure in both developed and developing regions, offering high cost-performance value.
Why Power Systems Prefer Oil-Immersed Transformers
The preference for oil-immersed transformers comes from their mature technology, economic advantages, and adaptability to various power system needs. Although dry-type transformers are gaining traction due to safety and environmental benefits, oil-immersed transformers remain the backbone of power grids worldwide because of their superior performance and cost efficiency.
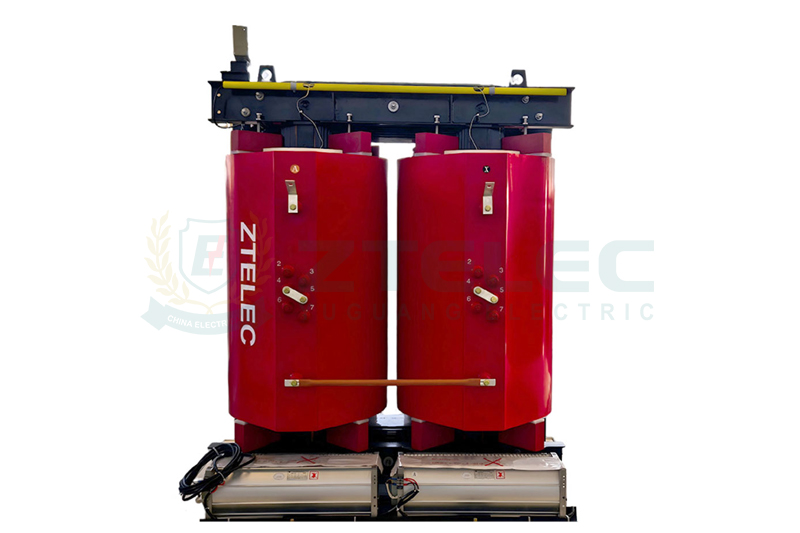
Comparison Summary: Oil-Immersed vs. Dry-Type Transformers
| Aspect | Oil Immersed Transformer | Dry Type Transformer |
| Cooling Medium | Insulating oil | Air or gas |
| Safety | Higher fire risk due to oil | Safer; no risk of oil-related fires |
| Maintenance | Requires regular oil testing | Minimal maintenance |
| Capacity | Suitable for large capacities | Limited to medium or low capacities |
| Installation | Outdoor or separate transformer rooms | Indoor-friendly |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |




