Cast Resin Dry-Type Transformer vs Vacuum Pressure Impregnated Transformer: Technology, Advantages, Applications
Time:2025-08-12 Auther:ZTelec-www.ztelectransformer.com
Cast Resin Dry-Type Transformers (CRT) and Vacuum Pressure Impregnated Transformers (VPI) are two leading dry-type transformer technologies. Instead of the liquid insulation used in oil-immersed transformers, both employ solid insulation materials, making them ideal for locations with strict fire safety standards and environmental requirements, such as high-rise buildings, metro systems, data centers, and critical infrastructure facilities.
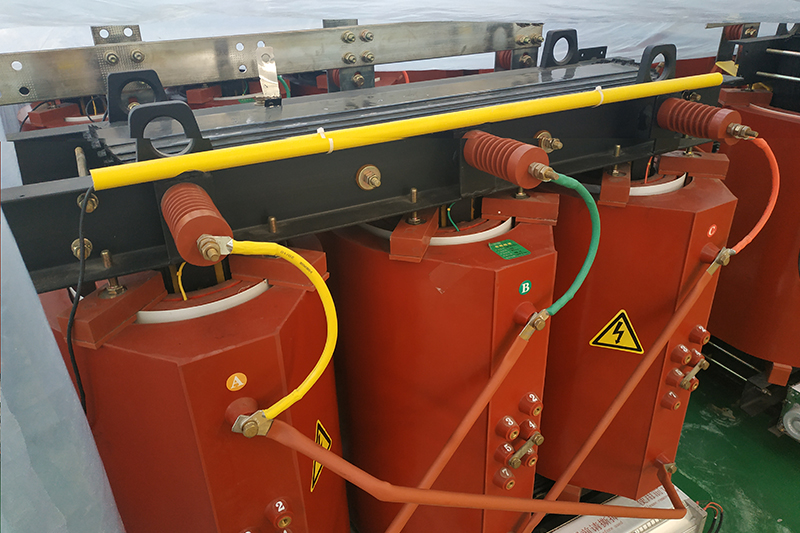

1. Technical Principles and Structural Features of Cast Resin Dry-Type Transformers
1.1 Insulation Process
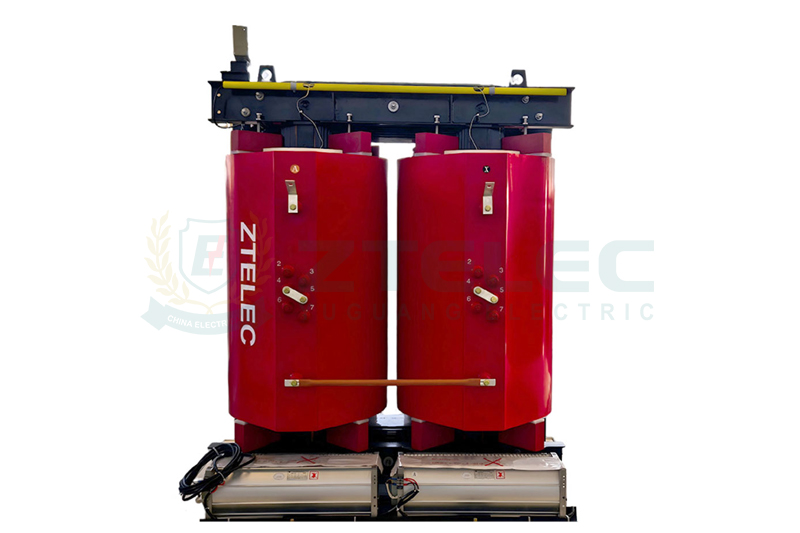
CRT transformers use epoxy resin vacuum casting technology to fully encapsulate high-voltage and low-voltage windings in a solid fiberglass insulation layer. This void-free design eliminates the risk of partial discharge. Key features include:
Vacuum Casting: Removes all air from windings, ensuring uniform resin distribution without bubbles or defects.
Foil Winding Design: High-voltage windings use aluminum foil with integrated casting; low-voltage windings use aluminum or copper foil. This ensures uniform voltage distribution, improved capacitance performance, and higher lightning impulse resistance.
Thin Insulation Layer: With only 1–3mm thickness (compared to 6mm in traditional designs), CRT offers better crack resistance and adaptability to extreme temperature changes.
1.2 Structural Advantages
Mechanical Strength: The cured epoxy resin forms a high-strength cylindrical structure with excellent short-circuit resistance.
Cooling Efficiency: Longitudinal ventilation ducts plus forced air cooling can increase rated capacity by 40%–50%.
Moisture & Fire Resistance: Flame-retardant and self-extinguishing resin allows safe operation in 100% humidity and enables immediate restart without drying.
2. Technical Principles and Structural Features of Vacuum Pressure Impregnated Transformers
2.1 Insulation Process
VPI transformers undergo a vacuum pressure impregnation process. After pre-baking to remove moisture, windings are placed in a vacuum to remove air, followed by pressurization with varnish to fill every gap in the insulation.
2.2 Structural Features
Windings are pancake-shaped, with insulation made from high-temperature materials like NOMEX paper. After impregnation, a uniform, thin insulation layer results in a lighter and more compact structure than CRTs.
2.3 Technical Advantages
High Permeability: Vacuum eliminates air resistance, pressure ensures varnish penetration, increasing insulation resistance by over 1,000 times.
Environmental Safety: Solvent-free varnish meets strict VOC emission standards.
Temperature Resistance: H-class insulation withstands 180°C, C-class with NOMEX paper withstands up to 220°C, ideal for high-temperature applications.
3. Advantages and Disadvantages
3.1 Cast Resin Transformer (CRT)
Advantages: Fully sealed, maintenance-free, >30 years lifespan, strong short-circuit resistance, eco-friendly, excellent in humid or corrosive environments.
Disadvantages: Higher cost due to epoxy resin and complex process, heavier structure, limited repairability (requires full winding replacement).
3.2 Vacuum Pressure Impregnated Transformer (VPI)
Advantages: Lower production cost for small and medium capacities, better heat dissipation, lighter, easier installation, higher repairability.
Disadvantages: Moisture resistance depends on process quality, requires periodic maintenance, lower mechanical impact strength than CRT.
4. Application Scenarios
4.1 CRT Applications
Ideal for high-end, mission-critical environments: data centers, large hospitals, airports, metro systems, mining, offshore oil platforms, and chemical plants.
4.2 VPI Applications
Best for commercial buildings, industrial plants, renewable energy stations, and cost-sensitive projects with stable environments.
When selecting between a Cast Resin Dry-Type Transformer and a Vacuum Pressure Impregnated Transformer, decision-makers must balance fire safety, mechanical strength, moisture resistance, cost, and maintenance needs. CRT is optimal for critical, high-risk environments, while VPI offers flexibility and cost efficiency for standard industrial and commercial use.




